- Sinch Community
- More topics
- Engage Classic
- Chatbot
- Build custom integrations using an API
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Chances are that you'll need to integrate bot with your back end or third-party services. Sinch Engage allows you to do that using APIs.
How custom integrations work
Engage Bot Builder offers a solution to integrate your conversational agent with your backend business logic, APIs, and databases. This integration allows you to create contextual, personalized, and actionable conversational experiences for your users.
The API is available in the Action step to enable you to create chatbot messages based on user-specific information and other external data. Additionally, it allows you to redirect your users to different conversational flows based on your own business logic. You can use this solution on any platform that supports receiving and responding to HTTP requests.
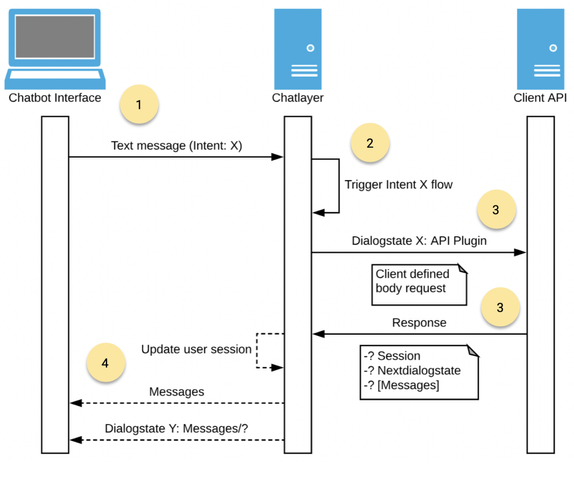
A user types and sends a text message from a conversational agent interface channel like WhatsApp, Webchat, Facebook Messenger, … to Engage bot builder.
The received message is going through Engage’s NLP engine to detect the intent and the returned intent combined with user context will be used to retrieve the next bot dialog in the conversation.
Engage’s API plugin can be added in a bot dialog to send an API request to your server with different types of static data and/or user session data.
Your server can respond with an object with three fields:
- session: A session object for saving retrieved user session data
- messages: An array of messages to send back to the interface channel
- nextDialogstate: A bot dialog state identifier to redirect the user to a next bot dialog state in a conversation flow.
Session data will first be stored in the user session so that you can use this data in messages defined in the array of messages or in messages defined in a dialog state defined as nextDialogstate in the API response. Second, messages will be sent, and afterwards the user is redirected to the nextDialogstate. All fields are optional.
API plugin
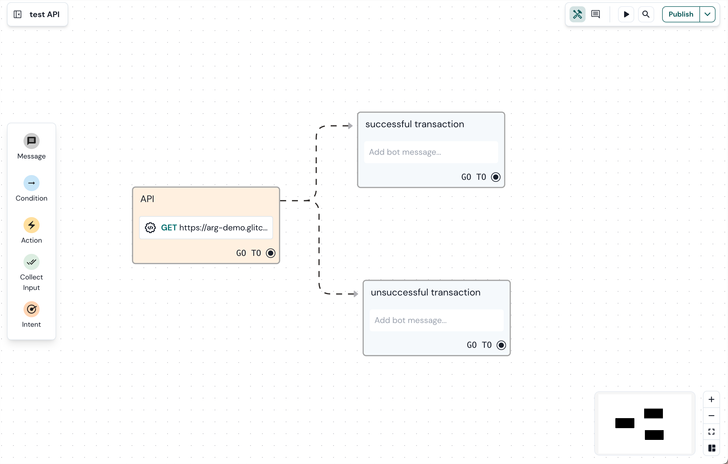
Engage bot builder provides an API plugin in the list of action plugins which you can configure in dialog state in one of your conversational flows.
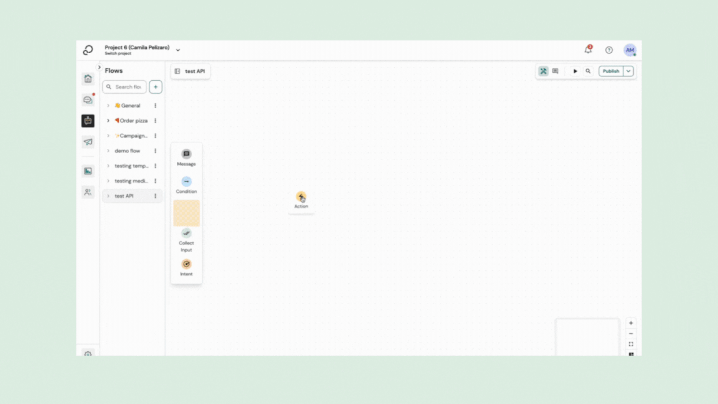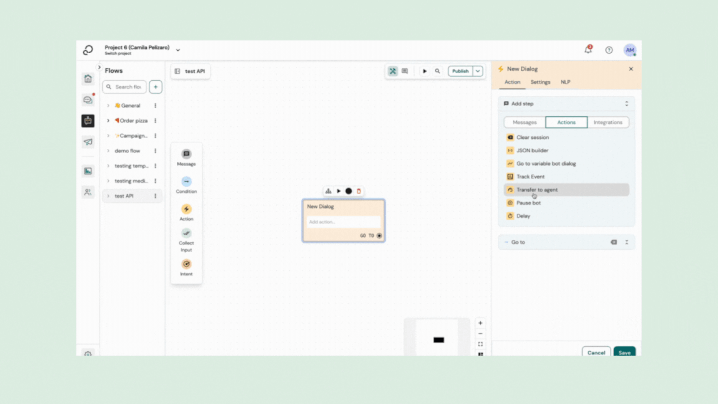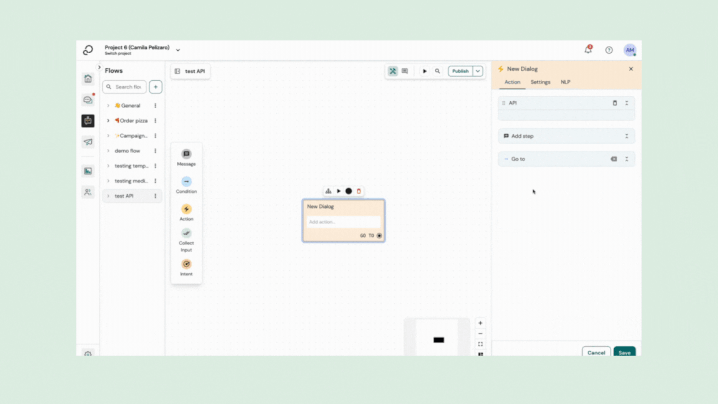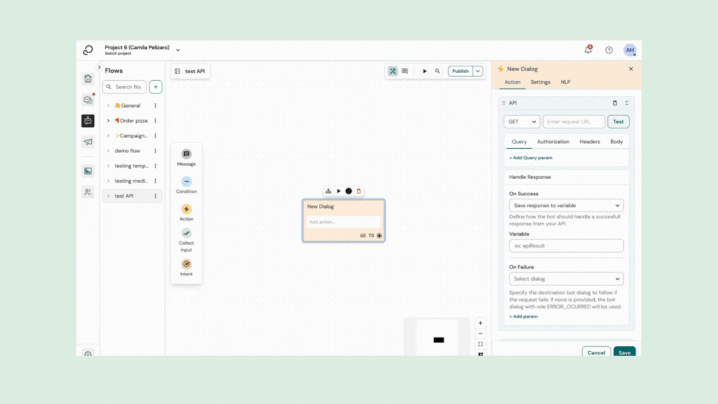
Sending the API request
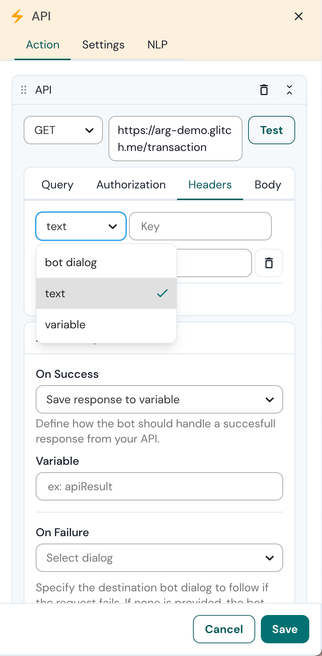
The API plugin sends a request to your back end server. It supports different configuration settings:
- HTTPS method
- API endpoint url
- Query parameters
- Body payload (JSON)
HTTPS method and API endpoint url
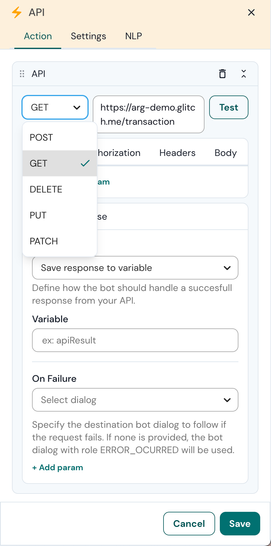
The plugin supports three HTTPS methods
- GET
- POST
- DELETE
- PUT
- PATCH
Query and body payload parameters
Add query parameters and/or a body payload by defining key value combinations. Each key can have three possible value types:
- text: static text
- variable: a user session variable. The value of the variable will be stored as value for the key. Dot and array notation are supported, for example: users[0].firstname
- dialogstate: select a dialog state from the dropdown. The dialog state id will be stored as value for the key. This id can be used to redirect the user to a certain dialog state based on your business logic when sending back the API response.
👉You can only define a request body when your request method is POST or DELETE.
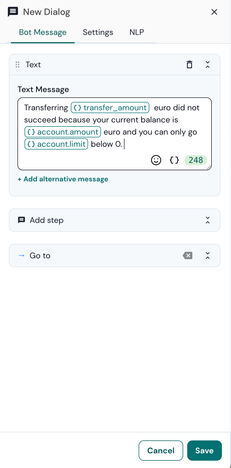
In this example, representing a money transfer, we send five keys in the body payload of an HTTPS POST request to our API endpoint.
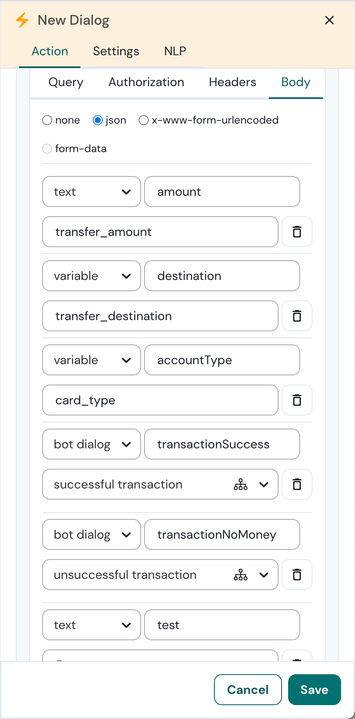
- The amount key will have the value of user session variable transfer_amount (ex: 500).
- The destination key will have the value of user session variable transfer_destination (ex: Elon Musk).
- The accountType key will have the value of user session variable card_type (ex: savings_account).
- The transactionSuccess key will have the dialog state identifier for the ‘successful transaction’ dialog state. This identifier can be used in the response of this API request to redirect the user to a new dialog state.
- The transactionNoMoney key will have the dialog state identifier for the ‘unsuccessful transaction’ dialog state. This identifier can be used in the response of this API request to redirect the user to a new dialog state.
- The test key will have a value of ‘5’.
This will result in the following body payload.
{
"amount": 500,
"destination": "Elon Musk",
"accountType": "savings_account",
"transactionSuccess": "successful transaction",
"transactionNoMoney": "unsuccessful transaction",
"test": 5
}
API headers
Next to Query and Body parameters, Engage bot builder also supports API Headers in its POST, GET and DELETE requests. Headers can be added using the same combination of Key, Type and Value as the other parameters.
Multi-language
If the API response will send agent messages back to the user and the agent supports multiple languages, don’t forget to send the user language in the request. The user language is available in the user session variable ‘locale'. Your back end service can use this language setting to send back the response in the user his preferred language.
Sending the API response
You do not need to configure the API plugin to listen for a response. This is done automatically and the API plugin will listen for what your API returns. The API plugin supports 3 types of return variables:
- session: A session object for saving data in to the user session. The session has two mandatory fields:namespace: a key namespace. The data object will be stored in this namespace key in the user session. You can access this object in Chatlayer.ai by using interpolation: *{namespace.dataKey}*data: an object which will be saved in the user session data in the namespace key.
- messages: An array of messages to send back to the user interface channel. The structure of different message types such as text, buttons, quick replies, carousels, lists, media, … is available in the chat message structure.
- action: an object defining an action such as redirecting the user to a next dialog state in the conversation.
- nextDialogstate: A dialog state identifier to redirect the user to a next dialog state in the conversation flow
The above 3 options are executed in the order shown above: session variables are set first, then messages are sent and then you will jump to the next dialog state. You can find an example JSON for these 3 cases in the code snippet below:
const result = {
session: {
namespace: 'myNamespace',
data: { variable: 'test123' },
},
messages: [{ type: 'text', config: { textMessages: [{ text: 'random message 1' }] } }],
action: {
nextDialogstate: 'dialogstate-123-abc',
},
};
👉Make sure you include the correct content t ype in the header: content-type: application/json;
Example
This example demonstrates one API endpoint for transferring an amount of money from an account type (regular or savings) to someone. We will redirected the user to a certain dialog state based on the transaction result.
app.post('/transaction', function (req, res) {
let nextDialogstate;
const { amount, destination, accountType, transactionSuccess, transactionNoMoney = req.body;
// get account type (regular - savings account)
const account = account_synonyms[accountType];
if( accounts[account].amount + accounts[accounthlimit — amount < ) {
nextDialogstate = transactionNoMoney
} else {
// transfer amount
accounts[account].amount —= amount;
nextDialogstate = transactionSuccess;
}
res.json({
action: {
nextDialogstate,
},
session: {
namespace: 'account',
data: {
limit: accounts[account].limit,
amount: accounts[account].amount
}
},
})
});
We receive the body payload object as defined in the API plugin. If the user doesn’t have a sufficient amount of money on his account we set the next dialog state to ‘transactionNoMoney’. Else we subtract the desired amount and set the next dialog state to ‘transactionSuccess'.
As a response for the request we send the next dialogs state to redirect the user to that state and we save the amount of money and the limit of his account in his session data under the namespace account. This data can be used in that next dialog state.
As an alternative solution you could also send that chat message as a response of the API plugin requests by using the messages key.
👉 For more API documentation, please check our API documentation here.
See also:
[New bot builder] Make a channel router flow
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content